[WapCar] Before explaining what types of differentials are there, let's first understand what a differential is?
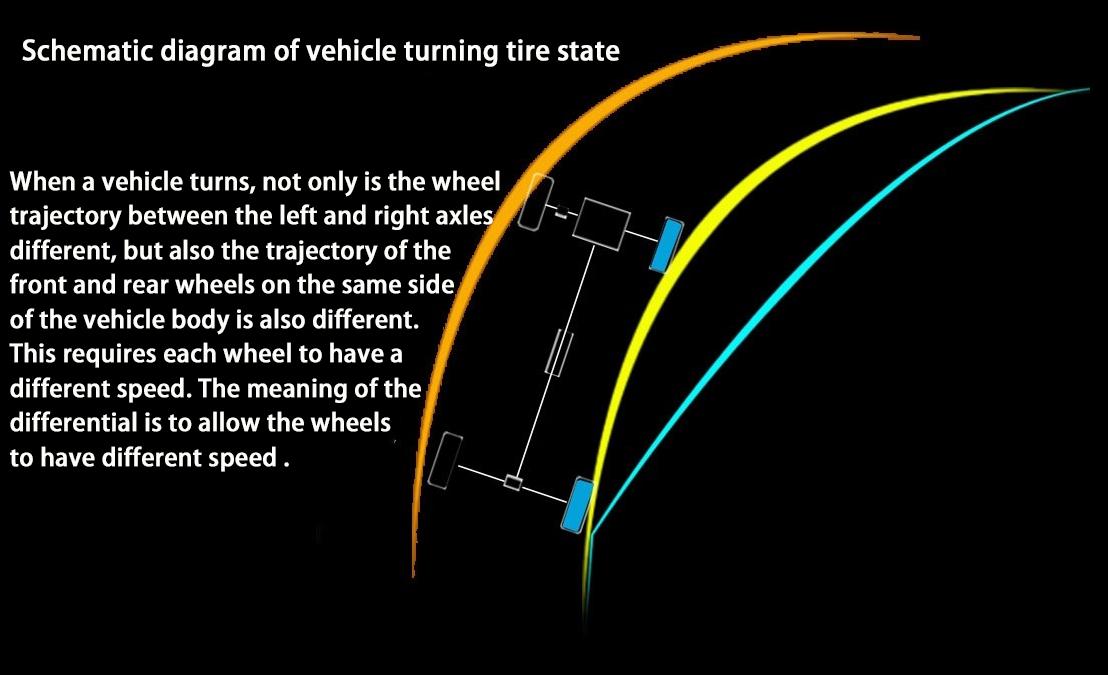
When turning, the driving trajectory of the wheels between the left and right half axles and the front and rear wheels of the same body are different. In the right-turning car as shown below, the curve is marked with yellow, and the blue wheel near the curve has a much smaller trajectory than the wheel on the side away from the curve. Therefore, if there is only one hard shaft connection between the two wheels, the outer wheels will have sliding friction due to the difference in speed when turning. This not only has poor ride comfort and poor vehicle stability, but also causes unnecessary wear and tear on the tires, and more importantly, it will affect the safety of the vehicle. Therefore, the differential appeared.
If there is no difference in speed or not large difference in speed between the wheels on both sides, the differential will not work. If the difference in speed between the wheels on both sides is too large, the gear set in the differential will work together to offset the difference in speed between the inner and outer wheels.
Open differential
Arrangement position: between front and rear axles, between left and right wheels
As the name implies, the open differential has no restrictions, it can be arranged between the front and rear axles and between the left and right wheels. Generally, the linear differential is arranged between the shafts, and the bevel gear differential is arranged between the wheels. If you find it difficult to understand, just remember that the planetary gear set of the open differential does not have any locking device, which is a prerequisite for the normal driving of the car.

When the adhesion between the wheels on both sides and the ground is unequal, the driving force of the wheels on both sides on the road can only depend on the side with the smaller adhesion. For example, when one side of the vehicle is slipping on an icy surface and the other side is on an asphalt road. The torque transmitted by the wheels on the asphalt road will not be greater than the wheel torque transmitted by the wheels slipping on the ice, which means that the vehicle cannot move forward.
Limited slip differential
Obviously, the vehicle needs to overcome wheel slip to get out of trouble, so the idea of restricting the slipping wheel came into being, and the following types of differentials can play a role in limiting wheel slip. At present, the common limited-slip methods on the market include electronic auxiliary braking system to play a limited-slip effect, multi-disc clutch-type limited-slip differential, torque-sensing limited-slip differential with worm mechanism, and limited-slip differential with viscous coupling shaft, mechanical lock type limited slip differential, etc.
1)Relying on electronic auxiliary braking system to play a limited slip effect
This kind of limited slip system uses the information collected by the wheel speed sensor and the information collected by other sensors to judge the working status of the wheels and the driving status of the vehicle. When it is detected that the wheels will slip or have slipped, ESP will brake the wheels, different brands of vehicles have different degrees of electronic limited slip, which is also one of the important factors that directly affect the vehicle's ability to escape difficulties.

The braking of the wheel by the electronic auxiliary system is equivalent to increasing the adhesion coefficient on the side of the slippery wheel, so that the effective torque transmitted to the wheel end is increased. As long as the "adhesion coefficient" brought by braking is higher than the adhesion coefficient of the outer wheels with adhesion, the differential can transmit enough driving torque to drive the outer wheels to rotate, thereby helping the vehicle to get out of trouble. Many urban SUVs have begun to use "brake" to distribute torque between wheels to help vehicles improve road performance and passing ability.
2)Multi-disc clutch type limited slip differential
Use position: between front and rear axles, between left and right wheels
There are generally two sets of friction discs inside the multi-plate clutch type limited slip differential, one is the driving disc and the other is the driven disc. The driving disc is connected with the front axle, and the driven disc is connected with the rear axle. The two sets of discs are immersed in special oil, and the combination and separation of the two rely on electronic system control.
Because the multi-disc clutch type limited slip differential has the advantages of fast response speed, instantaneous combination, electronic control combination, and no need for manual control, etc. It can be seen from the cheap and timely four-wheel drive SUV to the expensive full-time four-wheel drive SUV. In SUVs that emphasize passability or are positioned at high-end, low-speed gears are also added to the transfer case that is equipped with a multi-plate clutch-type limited-slip differential. It can play the role of torque amplification and can make up for the disadvantage of insufficient engine torque of the vehicle under complex road conditions.
-Full-time four-wheel drive with multi-disc clutch-type limited-slip differential

The above picture shows the four-wheel drive structure adopted by the Mercedes-Benz ML350, the transmission direction of the multi-plate clutch of the four-wheel drive system based on the horizontal engine layout is different, and its multi-plate clutch limited slip differential is responsible for distributing power to the front axle.


-Timely four-wheel drive with multi-disc clutch type limited slip differential


-Multi-disc clutch type limited slip differential arranged between left and right wheels

Although it has the advantages of fast response speed, instant integration, no manual control, etc, it is prone to overheating under high load, and due to non-"hard" connections, there are still shortcomings of slippage, which are unavoidable facts. Therefore, the four-wheel drive model equipped with this type of limited-slip differential is obviously not used for "surviving in the wild".
3)Torsen self-locking limited slip differential
Use position: between front and rear axles, between left and right wheels
The name Torsen is taken from the combination of the first few letters of the word Torque-sensing Traction, which means torque-sensing limited-slip differential. It can distribute the torque output according to the traction demand of each wheel, this distribution is done entirely by mechanical devices, and the response is rapid and accurate. The core of the whole system is the worm gear and worm meshing system, and the torque distribution is realized by the self-locking function of the meshing system.
Because the Torsen differential has the advantage of fast response, it is used by many vehicles in the central differential and the inter-wheel differential. So far, it has gone through the development of A, B, C, and three generations.



4)Viscous coupling limited slip differential
Use position: between front and rear axles
Viscous coupling differentials are usually installed on four-wheel drive vehicles based on front-wheel drive. Its characteristic is also that the power can be automatically distributed to the rear drive axle as needed without the driver's manipulation.

When the front wheel slips, there will be a large difference in speed between the front and rear wheels (the speed of the front wheels is much faster than that of the rear wheels). At this time, driven by the central drive shaft in the first half, the silicone oil inside the viscous coupling will be stirred. Based on its physical characteristics of thermal expansion, the clutch plate will be squeezed. Furthermore, the almost rigid connection state of the front and rear transmission shafts is realized, and the power lost by the idling of the front wheels can be transmitted to the rear wheels (Limited by the structure, this part of the power will not exceed 30% of the engine's output power at most).
The biggest disadvantage of this differential is that the four-wheel drive system has obvious hysteresis, and the efficiency of this power transmission method is not high. Therefore, the positioning of the vehicle using this differential is to drive on bad roads under simple conditions, and the high-strength non-paved road passability is obviously not its "specialty".
In addition, please note that vehicles equipped with this viscous coupling limited-slip differential are not allowed to tow by lifting the driving wheels. Since the device does not have the ability to completely cut off, if this method is used to tow, it just meets its limited slip condition (the front wheel does not move, the rear wheel rotates). The viscous coupling connects the front and rear transmission shafts, because the front and rear transmission shafts and their respective axles do not have the ability to differential, this will cause damage to the four-wheel drive system.
5)Mechanical lock differential
Use position: between front and rear axles, between left and right wheels
The above-mentioned limited slip is to partially restrict the relative rotation of the left and right wheels when one side of the vehicle is slipping, so that part of the engine torque is transmitted to the differential on the non-slip wheel. However, in most cases, due to the limited torque transmitted, there are still situations where it cannot help the vehicle to obtain sufficient traction to get out of trouble.
This type of differential can also be completely locked and unlocked without manual control by the driver, and has the advantages of simple structure, no need for gear oil containing special additives, and low maintenance costs. The familiar Eaton-style mechanical lock differential is one of the representatives.
The mechanical locking differential is further improved on the limited slip differential. In the case of one wheel slipping, the mechanical locking mechanism is triggered to completely lock the axle. 100% of the engine torque is transmitted to the effective wheels with grip, thereby providing enough traction to help the vehicle drive out of trouble.